Kicking off with Understanding Consumer Behavior, this opening paragraph is designed to captivate and engage the readers, setting the tone for a deep dive into the intricate world of consumer decision-making. From cultural influences to online shopping behaviors, get ready to unravel the mysteries behind why we buy what we buy.
Introduction to Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior refers to the study of how individuals make decisions to spend their available resources on goods and services. Understanding consumer behavior is crucial for marketers as it helps them tailor their strategies to meet the needs and preferences of their target audience.
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
- Cultural Factors: These include values, beliefs, customs, and traditions that shape an individual’s behavior. For example, a consumer from a collectivistic culture may prioritize family needs over personal desires.
- Social Factors: Social influences from family, friends, and society at large can impact consumer decisions. Peer pressure, social class, and reference groups all play a role in shaping consumer behavior.
- Personal Factors: Individual characteristics such as age, gender, occupation, lifestyle, and personality influence consumer choices. For instance, a young professional may prioritize convenience and time-saving products.
- Psychological Factors: These include perception, motivation, learning, attitudes, and beliefs that drive consumer behavior. Marketers use psychological insights to create appealing messaging and branding that resonates with consumers.
The Consumer Decision-Making Process: Understanding Consumer Behavior
In the consumer decision-making process, individuals go through several stages before making a purchase. These stages include need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior.
Need Recognition
Need recognition is the first stage in the consumer decision-making process where consumers identify a problem or need that triggers the decision to make a purchase. Marketers can influence this stage by creating awareness about their products or services through advertising, social media, or other promotional activities.
Information Search
During the information search stage, consumers gather information about different products or brands that could potentially satisfy their needs. Marketers can influence this stage by providing clear and detailed information about their offerings through websites, reviews, and other sources to help consumers make informed decisions.
Evaluation of Alternatives
In the evaluation of alternatives stage, consumers compare different products or brands based on factors like price, quality, and features. Marketers can influence this stage by highlighting the unique selling points of their products or services and showcasing how they stand out from competitors.
Purchase Decision
The purchase decision stage is where consumers make the final decision to buy a product or service. Marketers can influence this stage by offering promotions, discounts, or incentives to encourage consumers to make a purchase.
Post-Purchase Behavior
After making a purchase, consumers evaluate their decision and experience with the product or service. Marketers can influence post-purchase behavior by providing excellent customer service, addressing any issues or concerns promptly, and encouraging repeat purchases through loyalty programs or rewards.
Understanding Motivation and Perception
Motivation and perception play crucial roles in influencing consumer behavior. Motivation refers to the inner drive that prompts individuals to take certain actions, such as making a purchase. It is the force that guides consumer behavior and decision-making processes.
Types of Motivation
- Physiological Motivation: This type of motivation is driven by basic human needs, such as hunger, thirst, and shelter. Marketers often use appeals related to these needs to influence consumer behavior, such as food advertisements targeting hunger.
- Safety Motivation: Consumers are motivated by the need for security and protection. Products like insurance, alarm systems, and health-related items target this motivation.
- Social Motivation: People are motivated by the desire for social connections, belonging, and approval. Social media platforms and products that enhance social interactions tap into this motivation.
- Esteem Motivation: This type of motivation involves the need for recognition, respect, and prestige. Luxury brands and products cater to consumers seeking esteem and social status.
- Self-Actualization: The highest level of motivation involves the pursuit of personal growth, fulfillment, and realizing one’s potential. Products and experiences that promote self-improvement and personal development appeal to this motivation.
Perception in Consumer Behavior
Perception refers to how individuals interpret and make sense of the information they receive from the environment. It influences how consumers perceive products, brands, and marketing messages. Marketers can influence perception through various strategies, such as:
- Creating positive brand associations through advertising and branding efforts.
- Using sensory stimuli like colors, sounds, and textures to evoke specific emotions and reactions.
- Providing clear and consistent messaging to shape consumers’ perceptions of the product or brand.
- Utilizing influencers and testimonials to enhance the credibility and desirability of a product.
Consumer Buying Behavior
When it comes to consumer buying behavior, there are different types that impact marketing strategies. These include routine, limited, and extensive buying behavior, each influencing how consumers make purchasing decisions.
Types of Consumer Buying Behavior
- Routine Buying Behavior: Involves purchasing products or services on a regular basis with minimal decision-making. This type of behavior is common for everyday items like groceries or toiletries.
- Limited Buying Behavior: Occurs when consumers are familiar with a product category but may not have a preferred brand. They will research options before making a decision, often for more significant purchases like electronics or clothing.
- Extensive Buying Behavior: Involves consumers conducting thorough research and evaluation before making a purchase. This behavior is typical for high-involvement products like cars or real estate.
Influences on Consumer Buying Behavior
- Cultural Norms: Cultural values and beliefs can significantly impact consumer preferences and behaviors. Marketers must understand cultural differences to tailor their strategies effectively.
- Reference Groups: Consumers are influenced by the opinions and behaviors of reference groups, such as family, friends, or social media influencers. Marketers can leverage these groups to influence purchasing decisions.
- Social Class: Social class can influence consumer buying behavior by dictating preferences, priorities, and purchasing power. Understanding social class dynamics is crucial for targeting the right audience.
Brand Loyalty and Repeat Purchases
Brand loyalty plays a vital role in consumer buying behavior, as it leads to repeat purchases and customer retention. When consumers develop a strong attachment to a brand, they are more likely to continue buying from that brand, even if other options are available.
Online Consumer Behavior

In today’s digital age, online shopping has become increasingly popular among consumers, leading to a shift in consumer behavior compared to traditional offline shopping environments. Let’s delve into how consumer behavior differs in online versus offline settings, the impact of online reviews, social media, and influencers on purchasing decisions, and the concept of omnichannel retailing.
Consumer Behavior in Online vs. Offline Environments
Online shopping offers convenience, a wider selection of products, and the ability to compare prices easily, leading consumers to make more informed decisions compared to offline shopping. On the other hand, offline shopping provides a tactile experience, immediate gratification, and a chance to interact with products physically. Understanding these differences can help businesses tailor their marketing strategies to cater to the needs and preferences of consumers in each environment.
Impact of Online Reviews, Social Media, and Influencers
Online reviews, social media, and influencers play a significant role in shaping consumer purchasing decisions. Positive reviews can build trust and credibility for a product or brand, while negative reviews can deter potential customers. Social media platforms allow consumers to engage with brands directly, seek recommendations from peers, and stay updated on the latest trends. Influencers, with their large followings and influence, can sway consumer opinions and drive purchasing behavior.
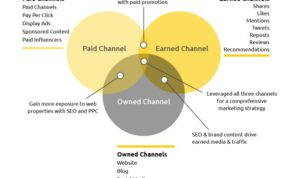
Omnichannel Retailing and Consumer Behavior, Understanding Consumer Behavior
Omnichannel retailing refers to the seamless integration of online and offline channels to provide a unified shopping experience for consumers. This approach allows consumers to research products online, make purchases in-store, or vice versa, creating a more personalized and convenient shopping journey. By offering multiple touchpoints for consumers to interact with a brand, businesses can enhance customer engagement, loyalty, and overall satisfaction.